Explore the fascinating lion characteristics, facts, from their impressive size to their unique social behavior and majestic manes.
Lions (Panthera leo) are among the most iconic animals on Earth, symbolizing strength and majesty. This article dives deep into their unique characteristics, combining scientific insights and captivating facts to help you understand why these big cats rule the wild.
Lions are the only truly social big cats, living in groups called prides (10–15 members). Key traits include:
Listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN, lion populations have declined by 43% over two decades. Key threats:
Support initiatives like anti-poaching patrols and habitat restoration.
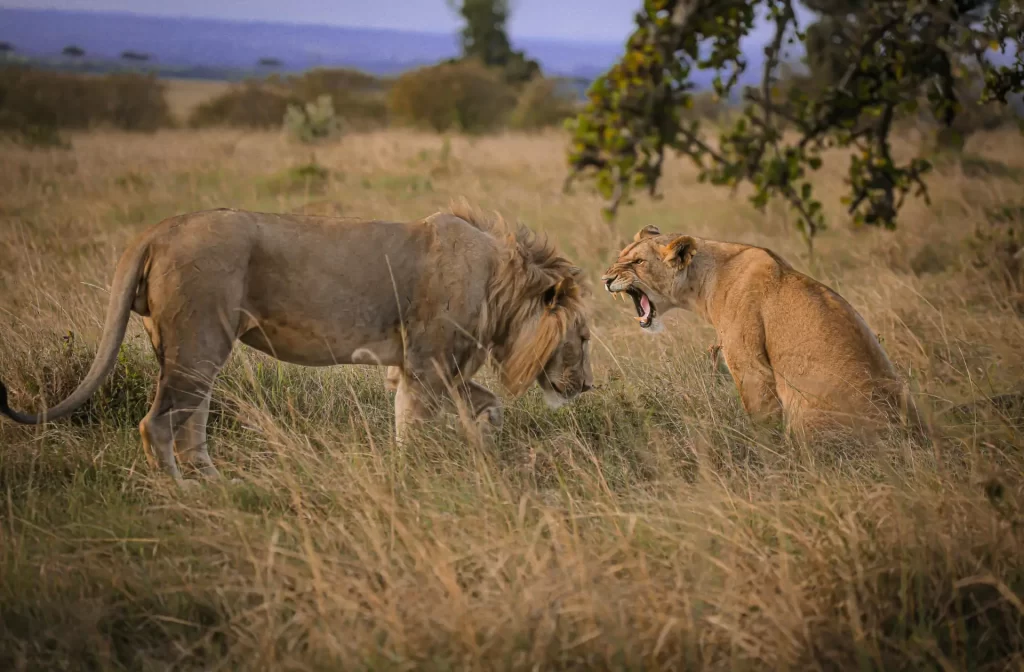

Manes indicate health and dominance. Darker, fuller manes attract more mates.
Lions sprint up to 50 mph but lack stamina for long chases.
They’re classified as Vulnerable, with only 20,000 left in the wild.
Lionesses handle 90% of hunting and cub rearing.
Some populations (e.g., in Tanzania) climb trees to avoid insects or survey territory.
Through roars, grunts, and scent markings.
Nndeeafrika partners with Africa’s top eco-tourism lodges/Camps to deliver luxury African safari that protect wildlife and empower local communities. Book your sustainable safari today.